第一章 Java-C(基础)
很多java初学者都有c的基础,但对java的博大精深还有所听闻,所以笔者专门分出一章叫java-c,c的读者会觉得非常轻松,所有的知识都在c中学过。这样会在刚接触java时, 有一种自然的亲近感。接着作者再献出两章叫java-c++(上),java-c++(下),对于有c++基础的同学(一般国内大学都开这课),也是个福利, 这样java就可以轻松入门。
2.java-c有什么重要的?
3.java好处
1)现在很多的大型网站,大数据分析等都是用java的架构搭建的,(比如Spring,Struts, hadoop)。
2)当前最火的安卓(android)手机的编程是用java, 够了吧!你有足够理由爱上java。
3)网页特效Ajax,jquery,ext,当前很多互联网公司和我书中后台也用java。
4)java职位和工程师最炙手可热, 薪资高。
4.java历史
1991年,Sun公司自行开发一种新的语言名为“Oak”。 1995年1月,Oak被更名为Java。这个名字来自于印度尼西亚有一个盛产咖啡的岛屿,中文名叫爪哇,意为世人端上一杯热咖啡。许多程序设计师从所钟爱的热腾腾的香浓咖啡中得到的灵感,因而热腾腾的香浓咖啡也就成为Java语言的标志。
1995年5月23日Java正式公布,以后人们对Java的兴趣和重视证明了这项技术将是主宰网络计算的未来:
5.Java语言的特点1.用java自带jdk开发第一个java程序: (视频下载) (全部书籍)
下面要讲的eclipse要想正常工作,需要先学会配置这里的jdk。jdk要想正常工作,需先学会配置JAVA_HOME和ClassPath和Path,可参见网站配套视频。MyFirstApp.java
public class MyFirstApp
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
System.out.println("This is my first Java Application!");
}
}
编译过程是:
F:\java教程\JiaXing\ch1>javac MyFirstApp.java
这个程序的输出为:
F:\java教程\JiaXing\ch1>java MyFirstApp
This is my first Java Application!
对上述实验现象的解释:Java程序的编译程序是javac.exe。javac命令将Java程序编译成字节码,然后你可用java解释器java命令来解释执行这字节码。
Java程序源码必须存放在后缀为.java的文件里。Java程序里的每一个类,javac都将生成与类相同名称但后缀为.class文件。编译器把.
class文件放在.java文件的同一个目录里,除非你用了-d选项。
我们先看看一个具体例子,给你们有个先入为主的感觉。
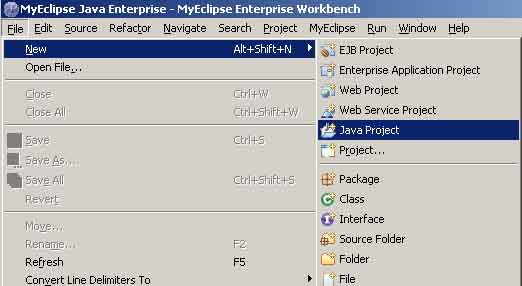
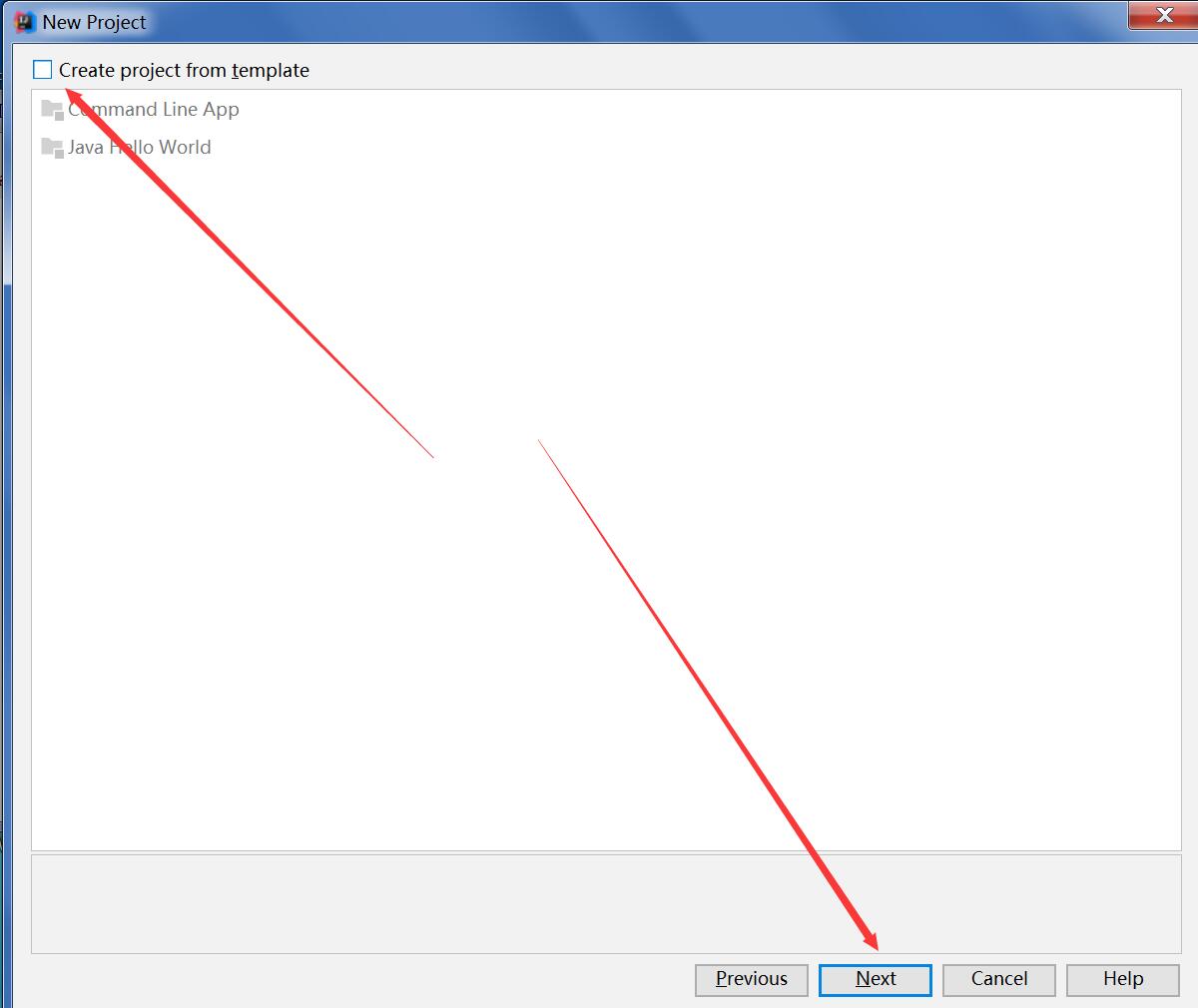
步骤一:在Eclipse开发工具中我们New一个java项目, 如图2_1

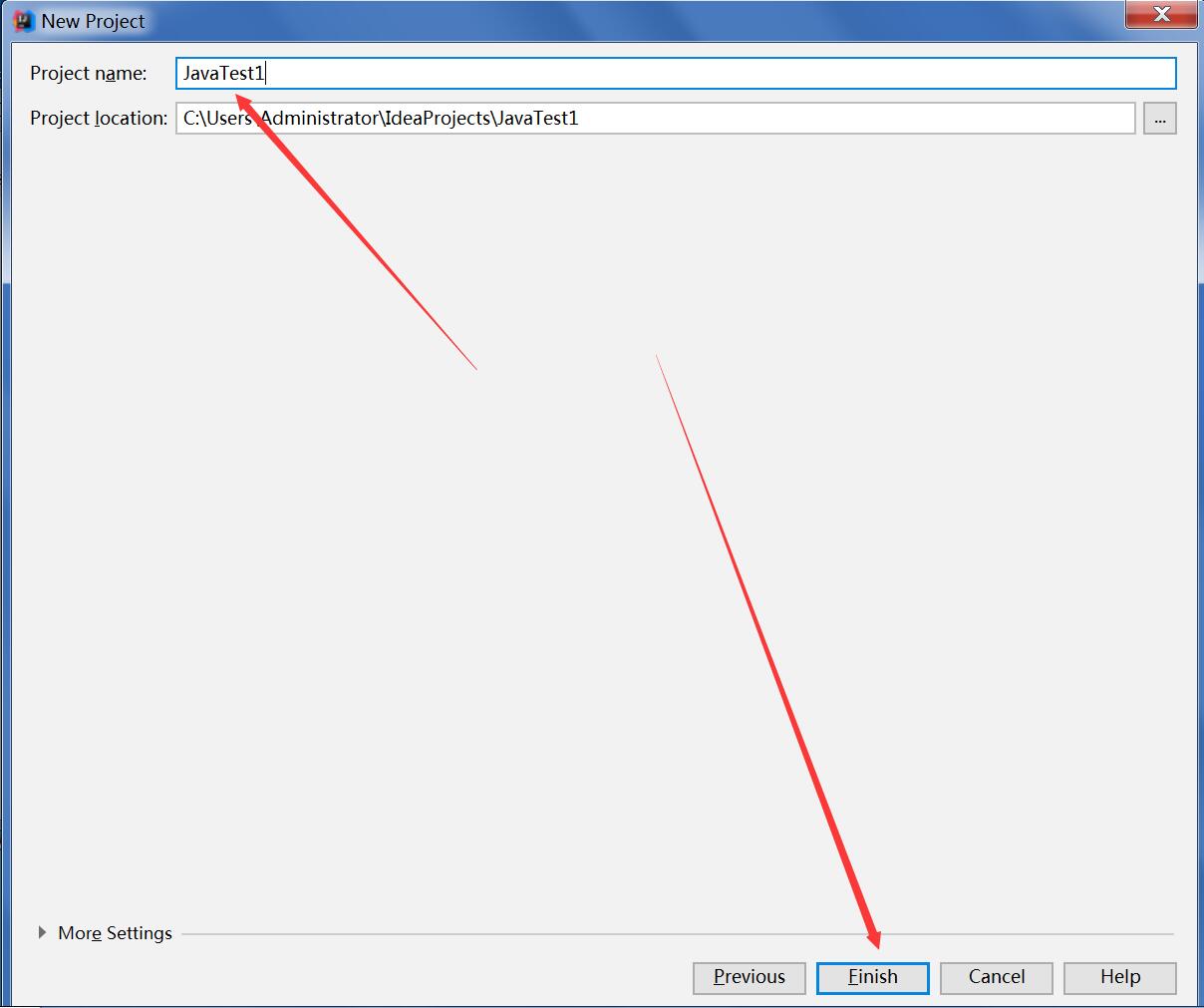
步骤二;给定一个项目名称Ch1Ex1如图2_2
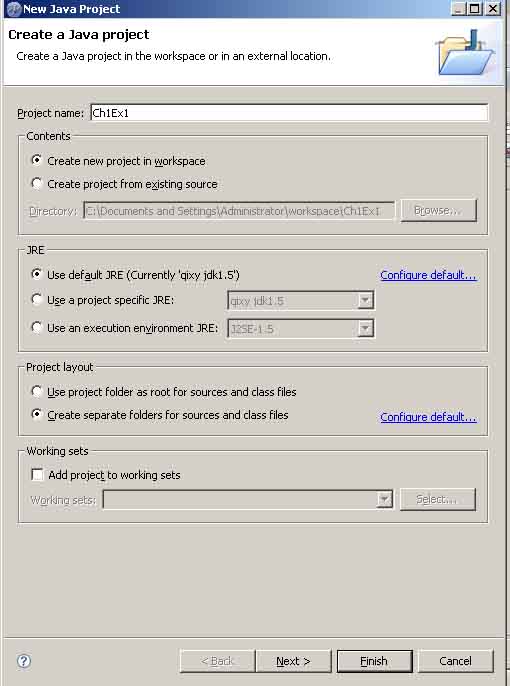
步骤三;点击finish结束(如图2_3), 建立一个java项目叫Ch1Ex1
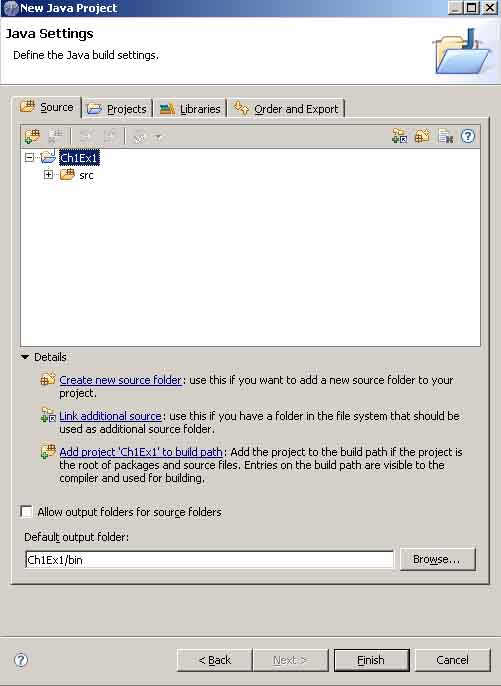
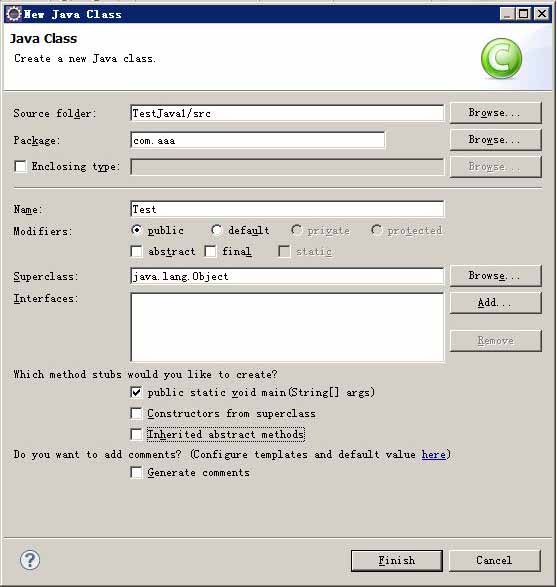
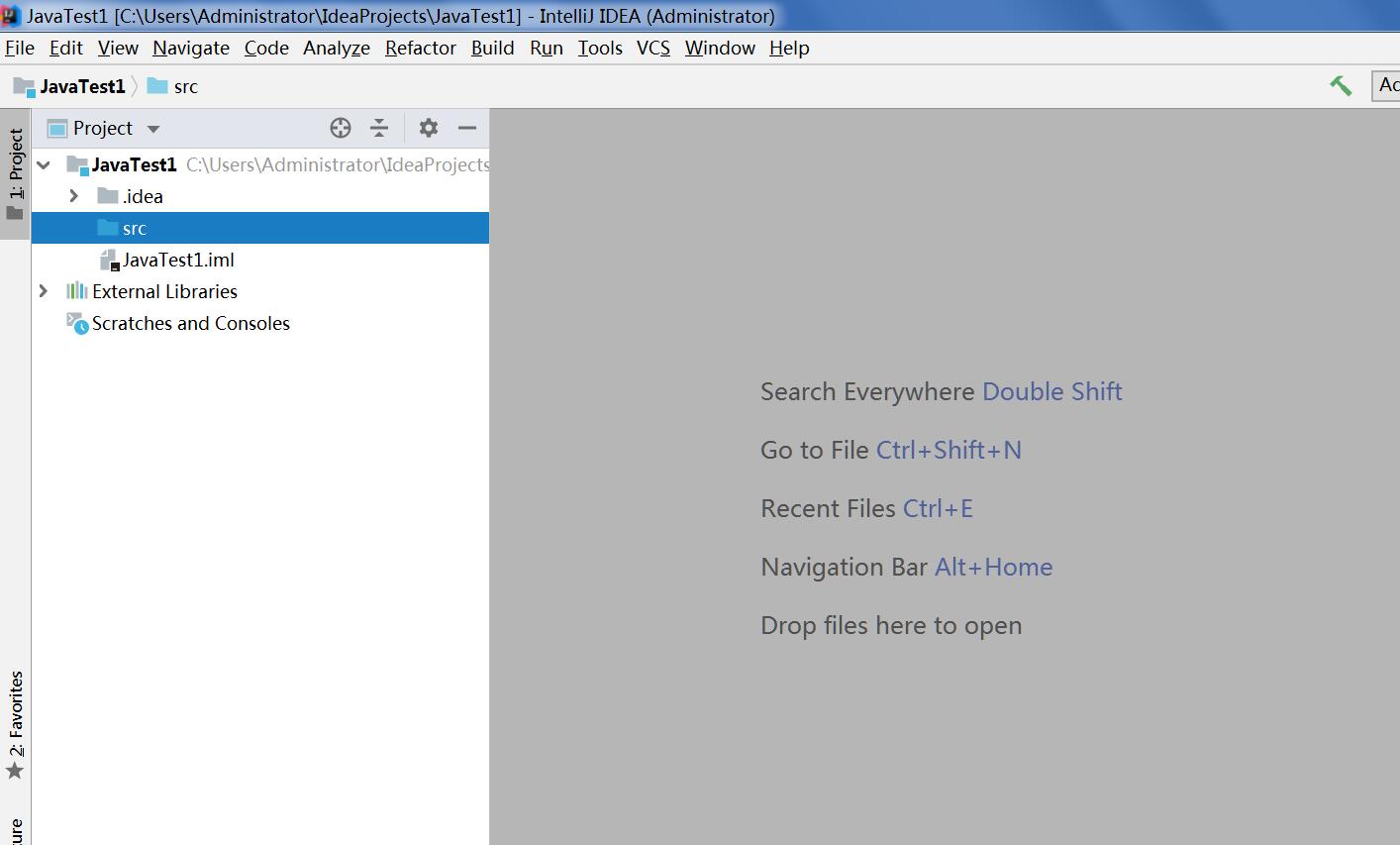
步骤四;在你新建Ch1Ex1当中new 一个class如图2_4
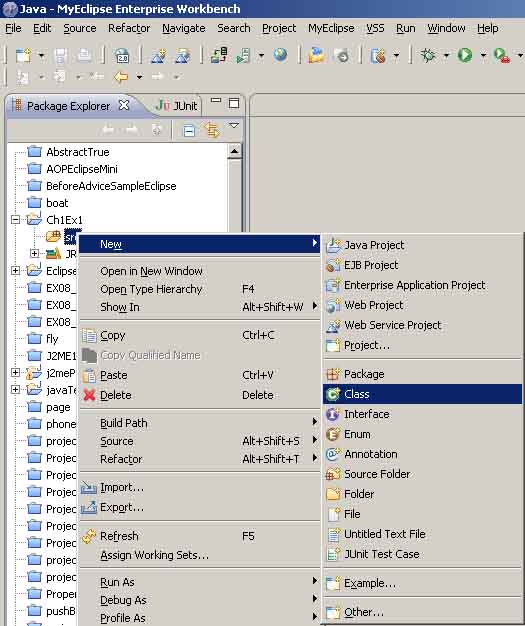
步骤五;建立一个类叫MyFirstApp,如图2_5
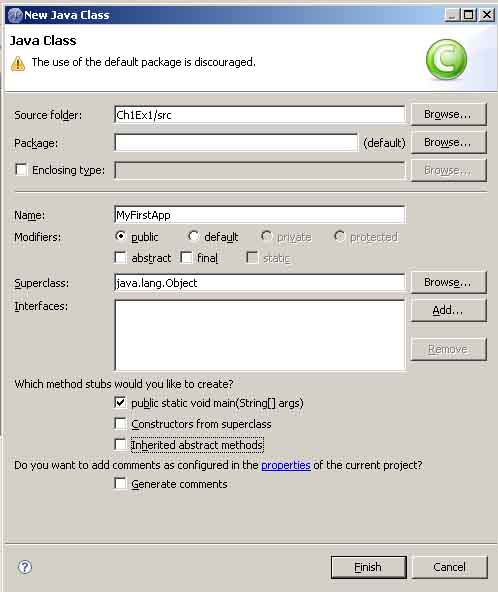
步骤六;新生成的类如图2_6
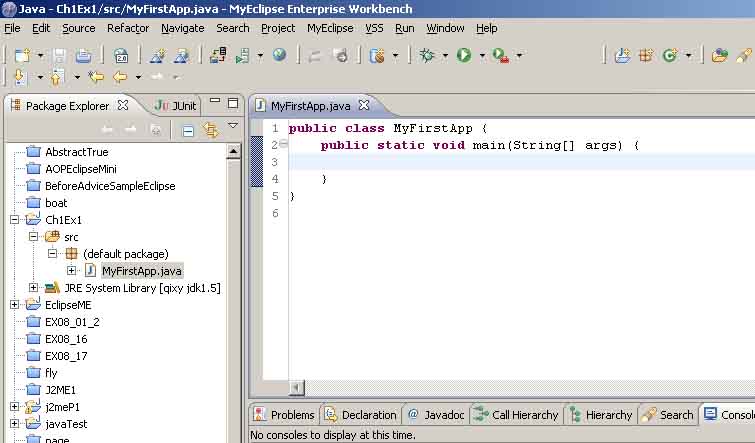
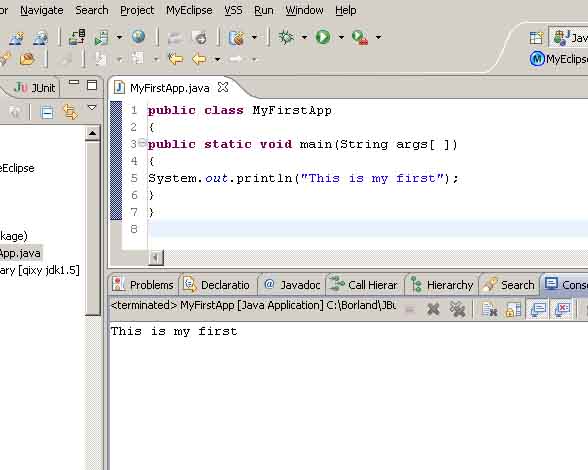
我们敲入代码如: \ch1\MyFirstApp.java:
public class MyFirstApp
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
System.out.println("This is my first");
}
}
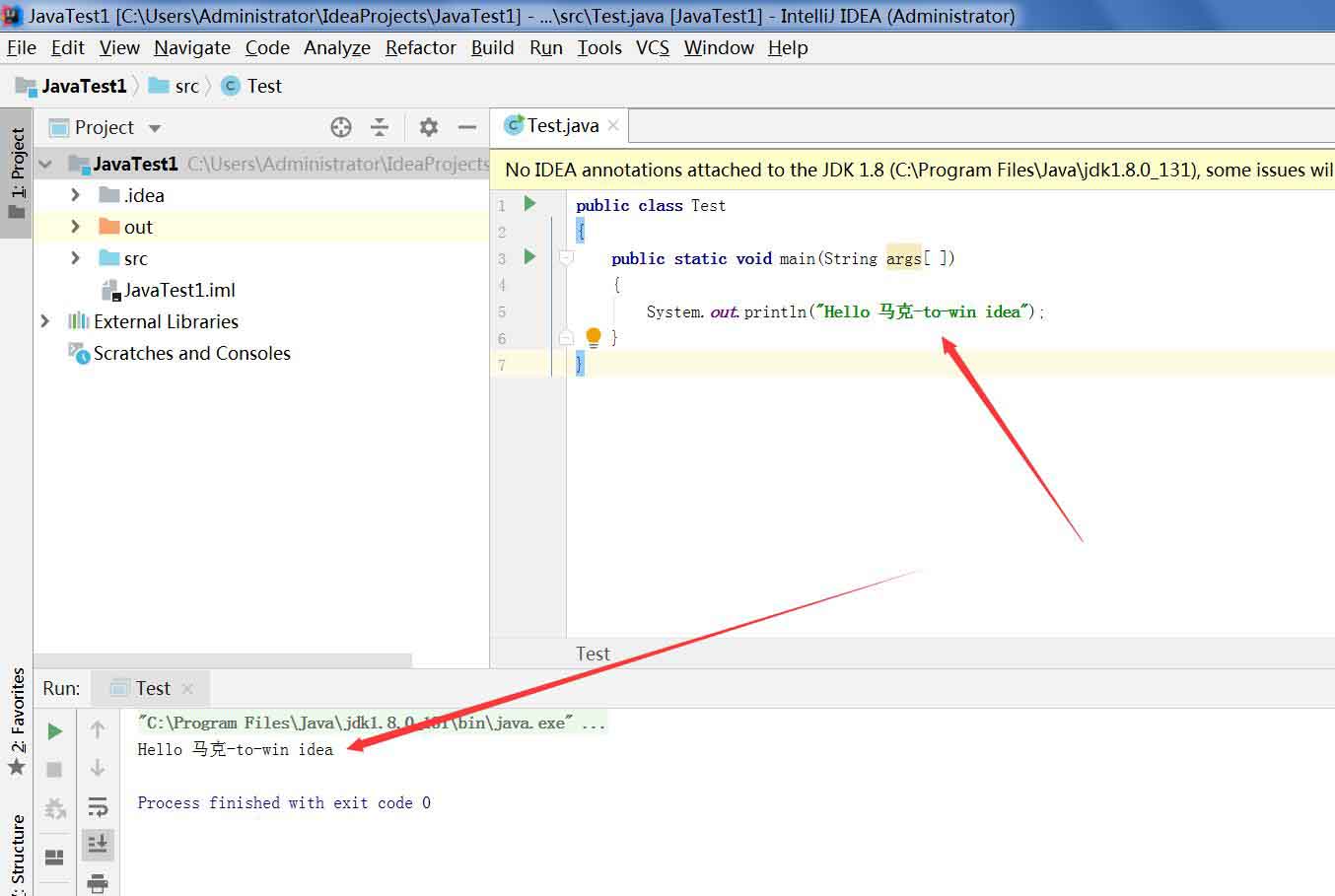
截图如图2_7
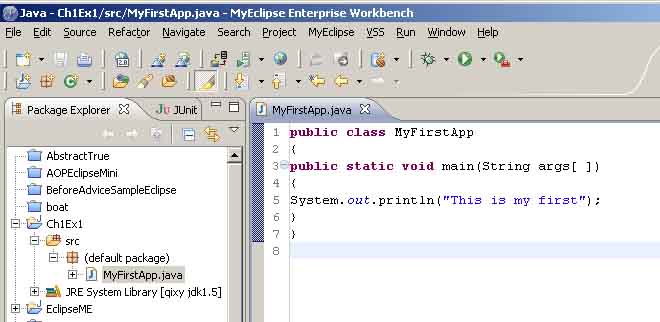
我们右击程序运行如图2_8
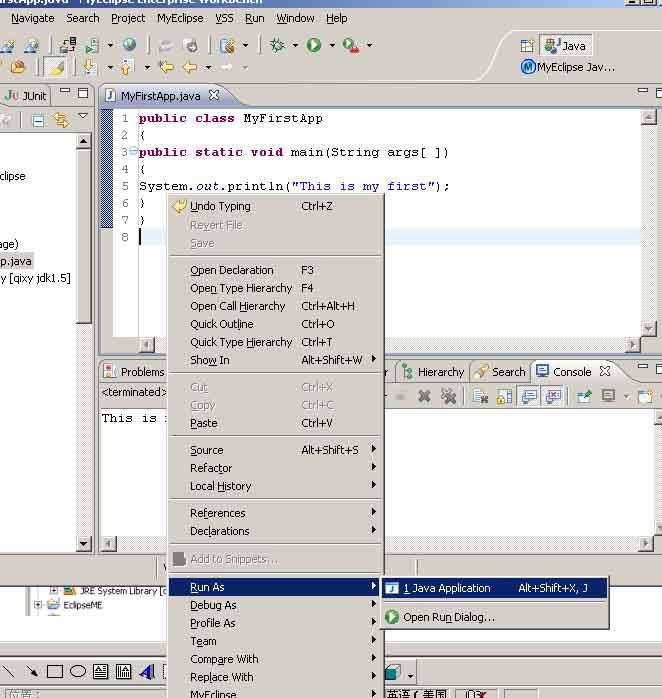
运行结果如图2_9
使用eclipse之前们需要先配置一下jdk。window/preference/java/installed JREs,详细请见视频。
我们书中(spring架构,ajax, android)都用eclipse3.62,所以我们还要说明在eclipse中运行helloworld! 在eclipse3.62中:
new/project/Java Project.
右击项目:new Class
(注意写完程序以后一定要存一下,有一次没存, 怎么都运行不出来)
第三节 Java-C语法
很多java初学者都有c的基础, 所以笔者专门分出一节叫java-c,c的读者会觉得非常轻松,所有的知识都在c中学过。
2.JAVA的注释
//注释内容 所有从//到行末的字符被忽略
/* 注释内容简介*/ 所有/* 和 */中的字符被忽略,能多行
3.变量
你可以在程序中使用变量来容纳数据。
你必须清楚地为你想在程序中使用地每一个变量提供一个名字和类型。变量声明,如下:
type name
int a;
变量的作用域是由变量声明位置决定的。
|
关键字 |
描述 |
大小/格式 |
|
整型 | ||
boolean | 布尔 | 1位 |
|
byte |
字节长度整型 |
8位 |
|
Short |
短整型 |
16位 |
|
int |
整型 |
32位 |
|
long |
长整型 |
64位 |
|
实数 | ||
|
Float |
单精度浮点型 |
32位 |
|
Double |
双精度浮点型 |
64位 |
|
其它类型 | ||
|
Char |
单个字符 |
16位(it is alleged that if it reads english character, it is smart enough to read only one byte. if it is chinese letter, it read two bytes. ) |
代码中直接为原始变量设置数值。
int anInt = 4;
下面是各种原始数值举例:
|
数值 |
类型 |
|
195 |
Int |
|
3344L |
Long |
|
34.78 |
Double(马克-to-win:based on wq's ppt,1.23 is double instead of float) |
|
34.78D |
Double |
|
34.78F |
float |
|
'd' |
char |
十进制 八进制 十六进制
0 0 0x0
4 04 0X4
十进制数可以用标准小数点或科学记数法表示。
如: 3.1334, 0.4, .6, 6.35e23, 2.234E8, 1.345e-19
单精度以32位存放,双精度以64位存放。
单精度 f/F后缀、双精度 d/D后缀表示。
如:3.6566f, 6.566e23D, 2.23F, 1.678e-19d
4.1 JAVA字符集
JAVA采用的Unicode字符集,它将ASCII码的8位字节扩展为16位,并扩充了ASCII字符集,使之增加许多非拉丁语字符。
Java中使用的是统一码(Unicode)。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte te = 25;
short rt = 50;
int er = 100;
long ng = 1000L;
float at = 1.34F; // remember the ‘F’!
double le = 1.34;
boolean an = true;
char c='我';
System.out.println("char: " + c);
System.out.println("Byte: " + te);
System.out.println("Short: " + rt);
System.out.println("Integer: " + er);
System.out.println("Long: " + ng);
System.out.println("Float: " + at);
System.out.println("Double: " + le);
System.out.println("Boolean: " + an);
}
}
the result is :
char: 我
Byte: 25
Short: 50
Integer: 100
Long: 1000
Float: 1.34
Double: 1.34
Boolean: true
一般讲,没有小数点的数就是整型。数字后面加一个'L' 或者'l'指定为一个长整型。一般用'L'而不用'l',因为'l'很容易与1'混起来。
数组、类以及接口是引用的类型。
4.2 变量名
变量名必须满足:
for example:
下面是一些无效的变量名:
2cou
hi-temp
No/ok
这里有个命名规范:变量名是以小写字母开头,而类名是以一个大写字母开头的。如果变量名包含了多个单词,而每个单词要组合在一起,则在每个单词的第一个字母大写,比如IsVisible(驼峰命名法)。而下划线(_)一般地只用于分离单词。
4.3 变量初始化
例子如下:
int a, b, c;
int d=5, e, f=5;
double pi = 3.45454;
char x = ‘v’;
char aChar = 'S';
boolean aBoolean = true;
final变量的数值不能在初始化之后进行改变(你希望a=3,有很多用到a的场合, 你当然不能在程序中就用3来代替a)。
比如:
final int h = 0;
想像有一个项目组主程序,定义了一个变量,PI=3.1415,他带两个初级程序员编程,这两个初级程序员通过继承类的方法来节省劳动,张三,想把PI改成3.1,李四想把PI改成3.142,这些都会报编译错误。final放在方法前,表示方法不能被覆盖。放于类前,表示类不能被继承。4.5 Number Type Casting(数字类型强转) (视频下载) (全部书籍)
隐式 casting(from small to big)
byte a = 111;
int b = a;
显式 casting(from big to small)
int a = 1010;
byte b = (byte)a;
注意: 从大到小必须强转!
一道著名的公司面试题如下,以下程序有何问题?
public class Test {上面这个程序,因为1是int,s1是short,所以s1+1就往大的隐形转,就自动变成int,所以这个式子s1 = s1 + 1;左边是short,右边是int, 当把大的变成小的时,需要强转。正确的程序见下:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
short s1 = 1;
s1 =(short) (s1 + 1);
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
输出结果:
2
4.6 转义符
换行 \n
水平制表符
\t
退格符
\b
回车符
\r
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i, k;
i = 10;
/*下面一句话的意义是:假如i小于零,k就等于-i,否则k就等于i*/
k = i < 0 ? -i : i; // get absolute value of i
System.out.print("Absolute value of ");
System.out.println(i + " is " + k);
i = -10;
k = i < 0 ? -i : i; // get absolute value of i
System.out.print("Absolute value of ");
System.out.println(i + " is " + k);
}
}
result is:
Absolute value of 10 is 10
Absolute value of -10 is 10
5.1 算术操作符
|
运算符 |
使用 |
描述 |
|
+ |
op1 + op2 |
op1 加上op2 |
|
- |
op1 - op2 |
op1 减去op2 |
|
* |
op1 * op2 |
op1乘以op2 |
|
/ |
op1 / op2 |
op1 除以op2 |
|
% |
op1 % op2 |
op1 除以op2的余数 |
这里注意,当一个整数和一个浮点数执行操作的时候,结果为浮点型。整型数是在操作之前转换为一个浮点型数的。
5.2 自增自减操作符
下面的表格总结自增/自减运算符:
|
运算符 |
用法 |
描述 |
|
++ |
a++ |
自增1;自增之前计算op的数值的。 |
|
++ |
++b |
自增1;自增之后计算op的数值的。 |
|
-- |
a-- |
自减1;自减之前计算op的数值的。 |
|
-- |
--b |
自减1;自减之后计算op的数值的。 |
5.3 Bitwise Operators(位运算符)
~
&
|
>>
<<
int a = 3; // 0 + 2 + 1 or 0011 in binary
int b = 6; // 4 + 2 + 0 or 0110 in binary
int c = a | b;//c=0111
int d = a & b;//d=0010
public static void main(String args[])
{
int k = 3; // 0 + 2 + 1 or 0011 in binary
int b = 6; // 4 + 2 + 0 or 0110 in binary
int c = k | b;//c=0111
int d = k & b;//d=0010
System.out.println("c @马克-to-win is "+c);
System.out.println("d is "+d);
}
}
5.4 关系运算符
>,>=,<,<=,==,!=5.5 逻辑运算符
如下表所示;
|
运算符 |
用法 |
什么情况返回true |
|
&& |
o1 && o2 |
Short-circuit(短路) AND, o1 和 o2都是true,有条件地计算o2 |
|
|| |
o1 || o2 |
o1 或者 o2是true,有条件地计算o2 |
|
! |
! o |
o为false |
|
& |
o1 & o2 |
o1 和 o2都是true,总是计算o1和o2 |
|
| |
o1 | o2 |
o1 或者 o2是true,总是计算o1和o2 |
public class Ternary{
static boolean doThing()
{
System.out.println("in doThing");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if((2>3)& doThing()) {
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
}
result is:
in doThing
public class Ternary{
static boolean doThing()
{
System.out.println("in doThing");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if((2>3)&& doThing()) {
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
}
result is:
什么结果也没有。
5.6 赋值运算符
i = i + 2;
可以这样简化:
i += 2;
上面的两行是等价的。
6.控制流程
6.1 if-else statement
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int num = 5;
int mod = num %2;
if (num ==0)
System.out.println(num + "是零");
else if (mod != 0)
System.out.println(num + "是一个奇数");
else
System.out.println(num + "是一个偶数");
}
}
result is:
5是一个奇数
变量可以是:variable can be:(mark: tried, can not be long)
char/int/short/byte(java1.7 就可以用String来switch了)
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
double d1=0.0, d2=0.0;
d1 = 11;
d2 = 22;
char o = '+';
switch(o){
case '+':
System.out.println(d1+d2);
break;
case '-':
System.out.println(d1-d2);
break;
case '*':
System.out.println(d1*d2);
break;
case '/':
System.out.println(d1/d2);
}
}
}
result is:
33.0
6.3 循环
6.3.1 while 循环
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int lim = 5;
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i<=lim){
sum =sum + i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
int j = 1;
while(j<=4){
System.out.println("j=" + j);
j++;
}
System.out.println(j);
}
}
result:
sum = 15
j=1
j=2
j=3
j=4
5
6.3.2 do-while循环
package com;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int lim = 0;
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
do{
sum =sum + i;
i++;
} while(i<=lim);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
6.3.3 for循环
break语句:从switch分支或循环中跳转出来,执行其后继语句。
continue语句:终止当前这一轮循环,继续下一轮。
(demo, also add in single step debug.)
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int lim = 4;
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=lim; i++){
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
the result is:
sum = 10
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=20; i>0; i -= 2){
System.out.println("The number is " + i);
}
for(int i=20; i<100; i *= 2){
System.out.println("The number is " + i);
}
/*
for(int i=10; i>0; i++){
System.out.println("无限循环");
}*/
}
}
the result is:
The number is 20
The number is 18
The number is 16
The number is 14
The number is 12
The number is 10
The number is 8
The number is 6
The number is 4
The number is 2
The number is 20
The number is 40
The number is 80
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int limit = 4;
long fac;
for (int i=1;i<=limit;i++){
fac = 1;
for (int j=2; j<=i;j++){
fac = fac*j;
}
System.out.println(i + "!" + " is " + fac);
}
}
}
the result is:
1! is 1
2! is 2
3! is 6
4! is 24
public class Continue{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5 || i==8){
continue;
}
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
}
result is:
i=1
i=2
i=3
i=4
i=6
i=7
i=9
i=10
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5 || i==8){
break;
}
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
}
数组是作为对象来实现的。(really occupy the memopry,真实的占用内存 )
An array is a data structure that stores a collection of value of the same type.(数组是一个数据结构,它存储一堆类型相同的值)
/*下面这句话只是宣称了一个参考类型的变量,而并没有真正初始化,this statement just declares the reference type variables, not yet initialize*/
int[] a;
string[] b;
char[] c;
/*下面这句话真正初始化了,也就是真正给数组分配了内存,Initialize: Allocate memory for the array.*/
a = new int[10];
b = new String[3];
c = new char[20];
int[] a;
a = new int[3];
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 2;
a[2] = 3;
System.out.println("the value of a[1] = " + a[1]);
a[1] = 100;
System.out.println("the value of a[1] = " + a[1]);
Initailizer(以下为另一种初始化数组的方法)
int[] a = {1,3,5,7,9};
Array length(数组的长度)
int i=a.length;//5
举例:
int array_int[ ];
String[ ] str;
利用new 来为数组型变量分配内存空间
array_int=new int[10];
str=new String[10];
两步可以合并,如:
String[ ] str=new String[10];
可以在它的length实例变量中找到一个数组的大小——也就是,一个数组能保存的元素的数目 。
所有的数组都有这个变量,并且它总是保存数组的大小。
8.1 数组的length
Length:数组的容量,而不是数组实际存储的元素的个数(mark,
during initialization,
the value of the array is initialized to 0, if the array 类型 is integer)。
// This program demonstrates the length array member.
class Length {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a1[] = new int[10];
int a2[] = {3,5,6,1,8,45,44,-10};
int a3[] = {4,3,2,1};
a1[1]=8;
System.out.println("length of a1 is " + a1.length);
System.out.println("length of a2 is " + a2.length);
System.out.println("length of a3 is " + a3.length);
}
}
J:\java教程>java Length
length of a1 is 10
length of a2 is 8
length of a3 is 4
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length==0){
System.out.println("you don't set command line parameters!");
}else{
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
System.out.println("args[" + i + "] is: " + args[i]);
}
}
}
}
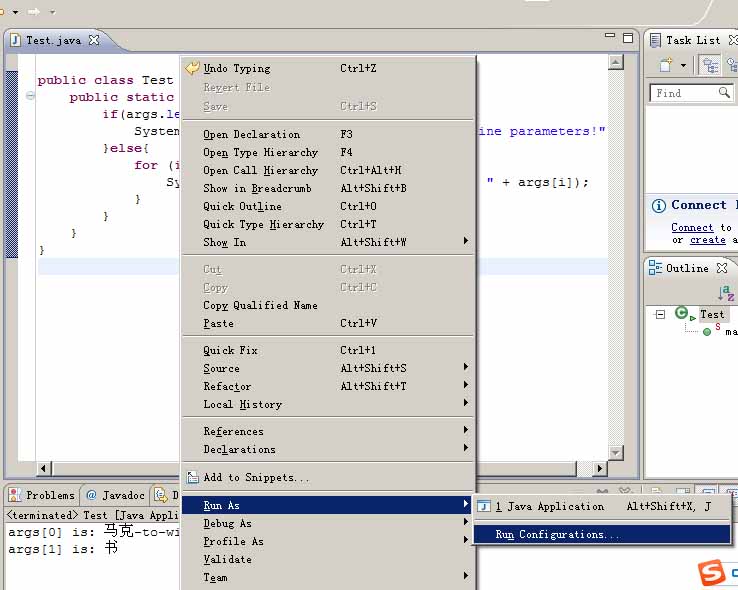
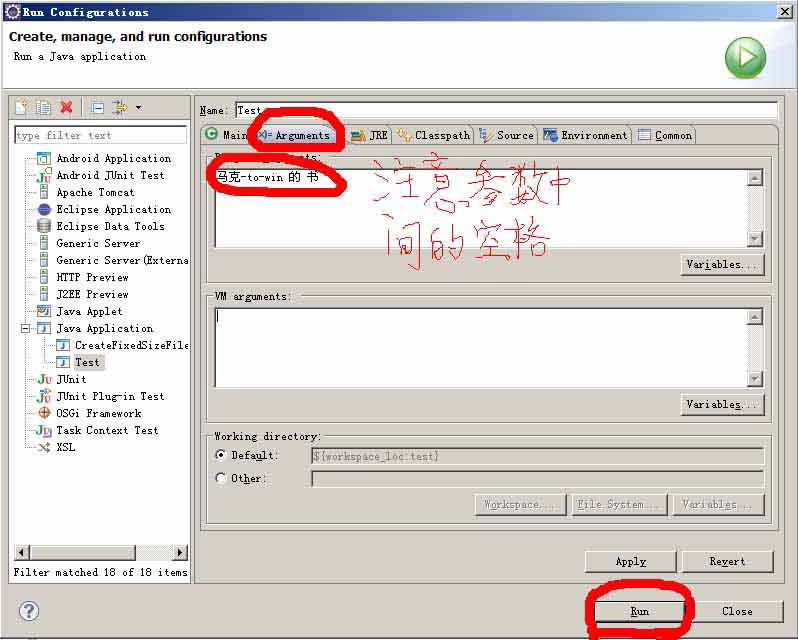
when use eclipse, don't "run as application",directly use "run configurations/run", then add in aguments in program arguments.(当运行eclipse,不要"run as application",而直接用"run configurations/run",然后加上参数在,program arguments.)
result is:
args[0] is: 马克-to-win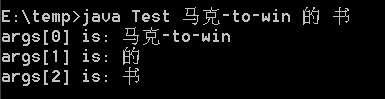
An array that contains other arrays as its elements.(一个数组中包含其他的数组作为它的元素)
public class TwoDimentional {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table= new char[2][4];
char[] row0 = {'A','B','Z','M'};
char[] row1 = {'C','D','K','L'};
table[0] = row0;
table[1] = row1;
for(int i=0; i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
System.out.println(table[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
result is:
A
B
Z
M
C
D
K
L
8.4 Nonrectangular Arrays(非矩形数组) (视频下载) (全部书籍)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[ ] str;
str=new String[2];
str[0]="aaa";
str[1]="bb";
String[ ] str1;
str1=new String[]{"aaa","bbb"};
// 假如写成下一句,就报这个错。Cannot define dimension expressions when an array initializer is provided
// str1=new String[2]{"aaa","bbb"};
System.out.println(str1[0]+str1[1]);
String[][] x = new String[3][];
x[0]=new String[]{"hello","马克-to-win"};
x[1]=new String[]{"are","you","fine"};
x[2]=new String[]{"ok"};
for(int i=0; i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<x[i].length;j++){
System.out.println("x["+i+"]["+j+"]"+" is "+x[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
结果:
aaabbb
x[0][0] is hello
x[0][1] is 马克-to-win
x[1][0] is are
x[1][1] is you
x[1][2] is fine
x[2][0] is ok
int add(int x, int y){
return x+y;
}
主调例子,
for example:
int result = add(5,3);
大家可以看出来和c语言是一样的。
7.1 Variable Scope(变量范围)
1)Class(类) scope
类中所有的方法都可以用
2)Block(块) scope
只在他声明的块中有效 or 嵌套的块儿中
3)Method(方法) scope
只在他声明的方法中有效
下例中,i是类变量,k 是块儿变量,j是方法变量,
public class Test{
static int i = 10;
public static void main(String[] args){
int j = 20;
int r = cube(i);
System.out.println(r);
r = cube(j);
System.out.println(r);
{
int k = 30;
r = cube(k);
System.out.println(r);
}
//r = cube(k);there is an error here.错误
}
static int cube(int n){
return n*n*n;
}
}
result is:
1000
8000
27000
7.3 方法重载(overload) (视频下载) (全部书籍)
当几个方法有相同的方法名,但参数个数不同或参数类型不同时,就涉及方法重载
方法重载有什么意义呢?在公司里编程,有时候一个方法名,要用到很多次,而且每次跟每次的参数都不一样,而且这个方法名,特别适合某个业务(比如登录),这个时候你变成其他的方法名,对大家来讲都很别扭,这时候就用到重载的概念了。
square(int i)和square(double d) 涉及方法重载。
7.2 About Method’s arguments(参数)
下面给出值传递 or 地址传递的例子, (视频下载) (全部书籍)
public class Test{
/*以下是值传递的例子,结果改不了,*/
public static void mod(int k){
k = k*k;
}
/*以下是地址传递的例子,结果会改变,*/
public static void mod(int[] x){
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++){
x[i] = x[i]*x[i];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 100;
int[] iArray = {1,2,3};
mod(i);
System.out.println(i);
mod(iArray);
for(int k=0; k<iArray.length; k++)
System.out.println(iArray[k]);
}
}
result is:
100
1
4
9
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 5;
System.out.println("5!=" + fac(5));
}
static long fac(long n){
/*fac(5)=5*4*3*2*fac(1)*/
if (n<=1){
return 1;
}else{
return n*fac(n-1);
}
}
}
result is:
5!=120
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int j=100; j<200; j++){
int k;
for(k=2; k<j; k++){
int tmp = j%k;
if (tmp == 0){
/*如果有一个k,能够除开j,就跳出内部到for循环*/
break;
}
}
/*能够来到这儿,说明或者,有k能除开j。或者从来没有k能除开过j。之后再
判断一下,j是否等于k,如果等于k,它就是质数。@马克-to-win*/
if(k==j){
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
}
结果:
1019.2 找出12和8的最大公约数和最小公倍数。 (视频下载) (全部书籍)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getcommon_mu(12,8);
getcommon_div(12,8);
}
//计算 最大公约数 和 最小公倍数
static void getcommon_mu(int n, int m) {
int i, b, d;
b = n > m ? n : m; //get big number,得到大数
d = n < m ? n : m; //get small number,得到小数
for (i = 1; i <=d; i++) {
/*假如12乘以2,能够除得开8的话。那12乘以2就是8的公倍数。*/
if ((i * b) % d == 0) {
System.out.println(" " + (i * b));
break;
}
}
}
static void getcommon_div(int n,int m){
int i, b, d;
b = n > m ? n : m; //get big number
d = n < m ? n : m; //get small number
for(i=d;i>=1;i--)
{
/*假如12能除的开4,而且8也能除的开4的话,4就是12和8的公约数。反正循环是为了得到最大公约数。马克-to-win*/
if((d%i==0)&&(b%i==0))
{
System.out.println(" "+i);
break;
}
}
}
}
结果:
24
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
String a = "I am a student whose age is 20";
shumu(a); //输出字符串空格和字母还有数字的数目。
}
static void shumu(String a) {
int shuzi = 0, zimu = 0, kongge = 0;
char[] c = new char[a.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length(); i++) {
/*下面这句话是java自带的函数,意思是对于某一个字符串,取出某个位置的字符。@马克-to-win*/
c[i] = (char) a.codePointAt(i);
if (c[i] >= '0' && c[i] <= '9') {
shuzi++;
}
if ((c[i] >= 'A' && c[i] <= 'Z') || (c[i] >= 'a' && c[i] <= 'z')) {
zimu++;
}
if (c[i] == ' ') {
kongge++;
}
}
System.out.println("数字的个数为: " + shuzi);
System.out.println("字母的个数为: " + zimu);
System.out.println("空格的数目为: " + kongge);
}
}
9.4 print out the following pattern(打印图案)。
*
***
*****
*******
*****
***
*
提示: 1)本题上面的图案和下面的图案是一样的。所以在打印上面图案的时候,把图案一行一行的都记录在数组b[i]当中。(hint: for the first half, the rule is 2n-1. record their pattern( the number of
their * asterisk and the number of space, then apply to the second half.but the
sequence is reverse.)
9.5 排序: (视频下载) (全部书籍)有一种排序的方法,非常好理解,详见本题的步骤,先找出最大值和最小值,把最小值打印出来后,把它存在另一个数组b当中,再删除此最小值,之后再来一次找出最小值,打印出最小值以后,再把它存在另一个数组b当中,再删除此最小值,这样循环往复,直到做完,你就会发觉,你已经把排了序数放在b数组当中了,而这里的彻底删除最小值的方法就是用比最大值还大一的数来取代最小值。(自己想想为什么?)参考后面的答案你会发觉,按照下面的四步,你已经把一个数组排序了。 i)make a method called getMin to find the minimal value of the array. ii)make a method called getMax to find the maximum value of the array. iii) replace the minimal value with the maximum+1. iiii) sort an array.
public class Test {
static int minPosition=0;//用这个全局变量来记录最小数的位置索引,
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 12, 7, 23, 4};
int max = getMax(a);
int[] b = new int[a.length];
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
int min = getMin(a);
/*把a数组当中最小的值,马克-to-win给替换成max+1,这样就相当于把原来的最小值从这个数组当中彻底清除掉了。整个循环做完,a数组就彻底废了。*/
a[minPosition] = max + 1;
minPosition=0;//把minPosition重置一下, 因为最小的位置已经不是这了。
b[j] = min;//用此方法a数组当中的数就一个一个从小到大捣到b数组当中了
}
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) System.out.println(b[j]);
}
static int getMax(int[] a) {
int max=a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length ; i++) {
if(max<a[i])
{
max=a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
static int getMin(int[] a) {
int min=a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length ; i++) {
if(min>a[i])
{
min=a[i];
minPosition=i;//用这个全局变量来记录最小数的位置索引,
}
}
return min;
}
}
结果是:
4
6
7
12
23
9.6 About string,"I am a teacher",这个字符串中有多少个字,且分别把每个字打印出来。
/*本题的思路就是,当我有一个字符串,我需要一个一个字符的处理,当下一个字符是个空格的时候,我就知道前面已
经构成了一个完整的字,把它输出出来就好了。如果发现下一个字符不是一个空格的话,我就把这个字符,加到另一个字符串中,逐渐积累那个字符串成为一个完整
的字。*/
public class Test {
static int amount_space = 0; //此变量用来记录空格的数量。the variable named amount_space is used to count the number of the space.
static int flag_Pro = 0; //此变量用来记录现在处理到大字符串中哪一个字符了。this pointer is used to remember the position where we look over.
static String newstring = "I am a teacher";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String outputword = "";
for (int i = flag_Pro; i < newstring.length(); i++) {
if (newstring.substring(i, i + 1).equals(" ")) { //假如newstring.substring(i, i + 1)马克-to-win,取出的字符是个空格,就执行这段程序。
System.out.println(outputword);
outputword = "";
amount_space++;
flag_Pro++; // and next time we will start at a new position
} else {//newstring.substring(i, i + 1);如果不是一个空格,就加到outputword中。
outputword = outputword + newstring.substring(i, i + 1);
flag_Pro++;
}
}
System.out.println(outputword);
outputword = "";System.out.println("共有"+amount_space+"个空格");
System.out.println("共有"+(++amount_space)+"个字");
}
}
结果:
I
public class MyFirstApp
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
System.out.println("This is my first Java Application!");
}
}
public class PrimitivesInAction{
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte aByte = 25;
short aShort = 50;
int anInteger = 100;
long aLong = 1000L;
float aFloat = 1.34F; // remember the ‘F’!
double aDouble = 1.34;
boolean aBoolean = true;
System.out.println("Byte: " + aByte);
System.out.println("Short: " + aShort);
System.out.println("Integer: " + anInteger);
System.out.println("Long: " + aLong);
System.out.println("Float: " + aFloat);
System.out.println("Double: " + aDouble);
System.out.println("Boolean: " + aBoolean);
}
}
the result is :
Byte: 25
Short: 50
Integer: 100
Long: 1000
Float: 1.34
Double: 1.34
Boolean: true
public class Ternary{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i, k;
i = 10;
k = i < 0 ? -i : i; // get absolute value of i
System.out.print("Absolute value of ");
System.out.println(i + " is " + k);
i = -10;
k = i < 0 ? -i : i; // get absolute value of i
System.out.print("Absolute value of ");
System.out.println(i + " is " + k);
}
}
result is:
Absolute value of 10 is 10
Absolute value of -10 is 10
class TernaryOp
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int salary,daysPresent = 30;
salary = (daysPresent == 20) ? 2000 : 3000;
System.out.println("您本月薪资为 $"+salary);
}
}
result is:
您本月薪资为 $3000
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 3; // 0 + 2 + 1 or 0011 in binary
int b = 6; // 4 + 2 + 0 or 0110 in binary
int c = a | b;//c=0111
int d = a & b;//d=0010
System.out.println("c @马克-to-win is "+c);
System.out.println("d is "+d);
}
}
public class Ternary{
static boolean doThing()
{
System.out.println("in doThing");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if((2>3)& doThing()) {
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
}
result is:
in doThing
public class Ternary{
static boolean doThing()
{
System.out.println("in doThing");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if((2>3)&& doThing()) {
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
}
result is:
什么结果也没有。
public class IfElseTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int number = 5;
int mod = number %2;
if (number ==0)
System.out.println(number + "是零");
else if (mod != 0)
System.out.println(number + "是一个奇数");
else
System.out.println(number + "是一个偶数");
}
}
result is:
5是一个奇数
public class MathOp{
public static void main(String[] args){
double d1=0.0, d2=0.0;
d1 = 10;
d2 = 20;
char op = '+';
switch(op){
case '+':
System.out.println(d1+d2);
break;
case '-':
System.out.println(d1-d2);
break;
case '*':
System.out.println(d1*d2);
break;
case '/':
System.out.println(d1/d2);
}
}
}
result is:
30.0
public class WhileLoop{
public static void main(String[] args){
int limit = 4;
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i<=limit){
sum =sum + i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
int j = 1;
while(j<=4){
System.out.println("j=" + j);
j++;
}
System.out.println(j);
}
}
result:
sum = 10
j=1
j=2
j=3
j=4
5
public class ForLoop1{
public static void main(String[] args){
int limit = 4;
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=limit; i++){
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
the result is:
sum = 10
public class ForLoop3{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=20; i>0; i -= 2){
System.out.println("The number is " + i);
}
for(int i=20; i<100; i *= 2){
System.out.println("The number is " + i);
}
/*
for(int i=10; i>0; i++){
System.out.println("无限循环");
}*/
}
}
the result is:
The number is 20
The number is 18
The number is 16
The number is 14
The number is 12
The number is 10
The number is 8
The number is 6
The number is 4
The number is 2
The number is 20
The number is 40
The number is 80
public class Factorial{
public static void main(String[] args){
int limit = 4;
long factorial;
for (int i=1;i<=limit;i++){
factorial = 1;
for (int j=2; j<=i;j++){
factorial = factorial*j;
}
System.out.println(i + "!" + " is " + factorial);
}
}
}
the result is:
1! is 1
2! is 2
3! is 6
4! is 24
public class Continue{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==4 || i==7){
continue;
}
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
}
result is:
i=1
i=2
i=3
i=5
i=6
i=8
i=9
i=10
public class VariableScope{
static int i = 10;
public static void main(String[] args){
int j = 20;
int r = cube(i);
System.out.println(r);
r = cube(j);
System.out.println(r);
{
int k = 30;
r = cube(k);
System.out.println(r);
}
}
static int cube(int n){
return n*n*n;
}
}
result is:
1000
8000
27000
public class Test22{
public static void modify(int k){
k = k*k;
}
public static void modify(int[] x){
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++){
x[i] = x[i]*x[i];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 100;
int[] iArray = {1,2,3};
modify(i);
System.out.println(i);
modify(iArray);
for(int k=0; k<iArray.length; k++)
System.out.println(iArray[k]);
}
}
result is:
100
1
4
9
public class SquareDemo{
public static int square(int i){
return i*i;
}
public static double square(double d){
return d*d;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=7;
double d = 20.9;
System.out.println("" + i + " squared = " + square(i));
System.out.println("" + d + " squared = " + square(d));
}
}
result is:
7 squared = 49
20.9 squared = 436.80999999999995
public class FactorialRecursion{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 5;
System.out.println("5!=" + factorial(5));
}
static long factorial(long n){
if (n<=1){
return 1;
}else{
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}
}
result is:
5!=120
class Length {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a1[] = new int[10];
int a2[] = {3,5,7,1,8,99,44,-10};
int a3[] = {4,3,2,1};
a1[1]=8;
System.out.println("length of a1 is " + a1.length);
System.out.println("length of a2 is " + a2.length);
System.out.println("length of a3 is " + a3.length);
}
}
J:\java教程>java Length
length of a1 is 10
length of a2 is 8
length of a3 is 4
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length==0){
System.out.println("you don't set command line parameters!");
}else{
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
System.out.println("args[" + i + "] is: " + args[i]);
}
}
}
}
result is:
args[0] is: 马克-to-win
public class TwoDimentional {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table= new char[2][4];
char[] row0 = {'A','B','Z','M'};
char[] row1 = {'C','D','K','L'};
table[0] = row0;
table[1] = row1;
for(int i=0; i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
System.out.println(table[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
result is:
A
B
Z
M
C
D
K
L
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] x = new String[3][];
x[0]=new String[]{"hello","马克-to-win"};
x[1]=new String[]{"are","you","fine"};
x[2]=new String[]{"ok"};
for(int i=0; i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<x[i].length;j++){
System.out.println("x["+i+"]["+j+"]"+" is "+x[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
结果:
x[0][0] is hello
x[0][1] is 马克-to-win
x[1][0] is are
x[1][1] is you
x[1][2] is fine
x[2][0] is ok
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int j=100; j<200; j++){
int k;
for(k=2; k<j; k++){
int tmp = j%k;
if (tmp == 0){
break;
}
}
if(k==j){
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
}
结果:
101public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getcommon_mu(12,8);
getcommon_div(12,8);
}
static void getcommon_mu(int n, int m) {
int i, b, d;
b = n > m ? n : m;
d = n < m ? n : m;
for (i = 1; i <=d; i++) {
if ((i * b) % d == 0) {
System.out.println(" " + (i * b));
break;
}
}
}
static void getcommon_div(int n,int m){
int i, b, d;
b = n > m ? n : m;
d = n < m ? n : m;
for(i=d;i>=1;i--)
{
/*马克-to-win*/
if((d%i==0)&&(b%i==0))
{
System.out.println(" "+i);
break;
}
}
}
}
结果:
24
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
String a = "I am a student whose age is 20";
shumu(a);
}
static void shumu(String a) {
int shuzi = 0, zimu = 0, kongge = 0;
char[] c = new char[a.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length(); i++) {
/*@马克-to-win*/
c[i] = (char) a.codePointAt(i);
if (c[i] >= '0' && c[i] <= '9') {
shuzi++;
}
if ((c[i] >= 'A' && c[i] <= 'Z') || (c[i] >= 'a' && c[i] <= 'z')) {
zimu++;
}
if (c[i] == ' ') {
kongge++;
}
}
System.out.println("数字的个数为: " + shuzi);
System.out.println("字母的个数为: " + zimu);
System.out.println("空格的数目为: " + kongge);
}
}
结果:
数字的个数为: 2
public class Test {
static int minPosition=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 12, 7, 23, 4};
int max = getMax(a);
int[] b = new int[a.length];
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
int min = getMin(a);
/*马克-to-win*/
a[minPosition] = max + 1;
minPosition=0;
b[j] = min;
}
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) System.out.println(b[j]);
}
static int getMax(int[] a) {
int max=a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length ; i++) {
if(max<a[i])
{
max=a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
static int getMin(int[] a) {
int min=a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length ; i++) {
if(min>a[i])
{
min=a[i];
minPosition=i;
}
}
return min;
}
}
结果是:
4
6
7
12
23
public class Test {
static int amount_space = 0;
static int flag_Pro = 0;
static String newstring = "I am a teacher!";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String outputword = "";
for (int i = flag_Pro; i < newstring.length(); i++) {
if (newstring.substring(i, i + 1).equals(" ")) {
if(!outputword.equals("")) {System.out.println(outputword);outputword = "";}
amount_space++;
flag_Pro++;
continue;
} else {
outputword = outputword + newstring.substring(i, i + 1);
flag_Pro++;
}
}
if(!outputword.equals("")) {System.out.println(outputword);outputword = "";}
System.out.println("共有"+(++amount_space)+"个字");
}
}
结果:
4